Python ETL Project: Scraping, Transforming, and Loading Book Data
📌 Overview
This project is a complete ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipeline built in Python, which prepares a structured dataset from an unstructured source.
It scrapes book data from the web, cleans and normalizes it, and loads it into a SQL database, producing an analytics ready dataset. The goal of this project is to demonstrate a practical, end-to-end data engineering ETL workflow using Python and containerization with Docker.
Key Features:
- Automated Data Extraction
- Data Cleaning and Quality Control
- Relational Database Schema Desing
- Containerized Deployment
- Analytics Ready
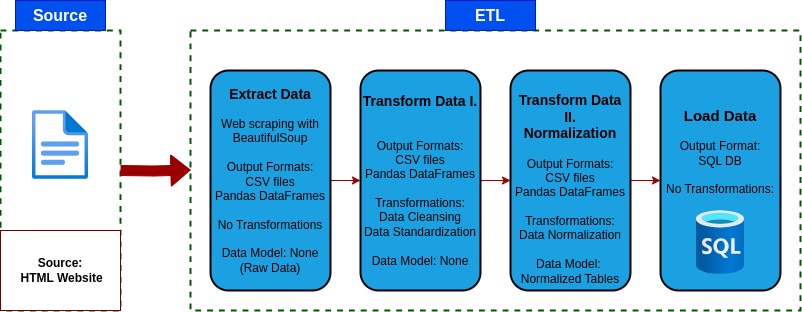
⚙️ ETL Pipeline Steps
1️⃣ Extract
- Scrapes all catalog pages from Books to Scrape.
- Retrieves metadata: title, genre, rating, price, stock availability, UPC, and number of reviews.
- Saves raw data to 1_extract_raw_data.
2️⃣ Transform
- Removes duplicates and null values.
- Standardizes data types and formats.
- Reclassifies Default and Add a comment genre into Uncategorized.
- Maps rating strings to numerical values.
- Cleans currency symbols and parses stock quantities.
- Saves cleaned data to 2_transform_data/books_cleaned_data.csv/books_raw_data.csv.
3️⃣ Normalize
- Extracts a genre lookup table.
- Replaces genre strings with foreign key IDs.
- Splits in_stock data into its own table.
- Saves normalized CSV files to 3_normalized_data/.
4️⃣ Load
- Loads normalized tables into a SQL database.
- Creates database and tables if they don’t exist .
-
Truncates tables and applies full load.
🐳 Docker Support
-
v2.0 – Python, PostgreSQL & Docker Compose Integration
The ETL pipeline is containerized with Docker Compose for multi-container deployment, including:
PostgreSQL database as backend.
Python ETL container.
Clone the repository and navigate to the project directory:
git clone https://github.com/danielv089/bookstore-etl-pipeline-project.git cd bookstore-etl-pipeline-project/v2.0_postgres_docker_composeBuild and start the containers:
docker compose up --buildThis will start a PostgreSQL container and then run the ETL container to extract data.
PostgreSQL connection is configured via environment variables in docker-compose.yml
PostgreSQL data is stored in the pgdata named perstistent volume.
Data inside the PostgreSQL container:
postgres=# \l List of databases Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | ICU Locale | Locale Provider | Access privileges ---------------+----------+----------+------------+------------+------------+-----------------+----------------------- books_website | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.utf8 | en_US.utf8 | | libc | postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.utf8 | en_US.utf8 | | libc | template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.utf8 | en_US.utf8 | | libc | =c/postgres + | | | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.utf8 | en_US.utf8 | | libc | =c/postgres + | | | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres (4 rows) books_website=# \dt public | books | table | postgres public | genres | table | postgres public | in_stock | table | postgres books_website=# SELECT COUNT(*) FROM books; count ------- 1000 (1 row) books_website=# SELECT * FROM books LIMIT 5; upc | titles | genre_id | ratings | product_type | price_excl_tax_gbp | price_incl_tax_gbp | tax | num_reviews ---------------------------+---------------------------------------+----------+---------+--------------+--------------------+--------------------+------+------------- a897fe39b1053632 | A Light in the Attic | 32 | 3 | Books | 51.77 | 51.77 | 0.00 | 0 90fa61229261140a | Tipping the Velvet | 20 | 1 | Books | 53.74 | 53.74 | 0.00 | 0 6957f44c3847a760 | Soumission | 16 | 1 | Books | 50.10 | 50.10 | 0.00 | 0 e00eb4fd7b871a48 | Sharp Objects | 25 | 4 | Books | 47.82 | 47.82 | 0.00 | 0 4165285e1663650f | Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind | 21 | 5 | Books | 54.23 | 54.23 | 0.00 | 0 (5 rows) -
v1.5 – Python, SQLite and Docker
This ETL pipeline is containerized for easier deployment.
Build the Docker image:
docker build -t v1.5_sqliteRun the Docker container with volumes to map folders inside the container to folders on the host machine:
docker run -it --rm -v "$PWD/data":/app/data -v "$PWD/logs":/app/logs v1.5_sqlite
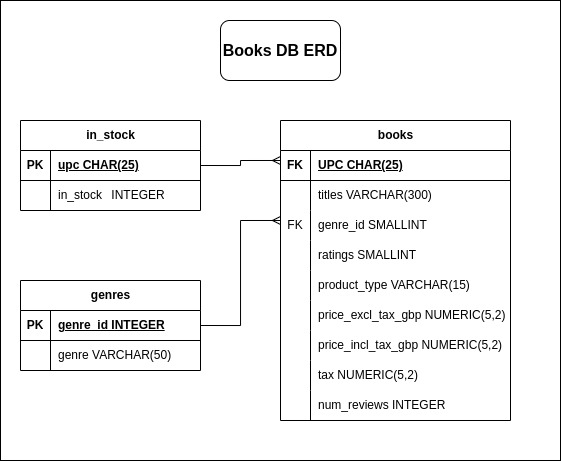
🗃️ ERD Diagram
🧰 Tech Stack
- Python
- Pandas
- Requests
- BeautifulSoup4
- SQLite3
- Logging
- Docker
- Pytest
- PostgreSQL
- Psycopg
📁 V2.0 Folder Structure
── v2.0_postgres_docker_compose
├── data
│ ├── 1_extract_raw_data
│ │ └── books_raw_data.csv
│ ├── 2_transform_data
│ │ └── books_cleaned_data.csv
│ ├── 3_normalized_data
│ │ ├── books.csv
│ │ ├── genres.csv
│ │ └── in_stock.csv
│ └── postgres_dump_data_sql
│ └── books.sql
├── docker-compose.yml
├── Dockerfile
├── etl
│ ├── extract.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── load.py
│ ├── logger.py
│ ├── normalize.py
│ └── transform.py
├── logs
│ └── pipeline_logs.txt
├── main.py
├── requirements.txt
└── tests
└── test_etl.py
🔗 References
-
Books to Scrape https://books.toscrape.com/
-
Pandas Documentation https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/
-
BeautifulSoup Documentation https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/
-
Requests Library https://docs.python-requests.org/
-
SQLite3 https://docs.python.org/3/library/sqlite3.html
-
Python Logging Module https://docs.python.org/3/library/logging.html
-
Docker Documentation https://docs.docker.com/
-
PostgreSQL Documentation https://www.postgresql.org/docs/
-
Psycopg Documentation https://www.psycopg.org/
✅ This project uses only publicly available data for educational purposes.
